A RAM slot, also known as a RAM socket, is a long, slim slot on the motherboard of a PC. This allows a RAM module of varying speeds and capacities to be accommodated. Most motherboards have either two or four of these memory banks. Each slot has a maximum RAM capacity, usually between 8 and 32 gigabytes depending on your CPU and motherboard combination.
The RAM slots on modern motherboards are numbered. This way you know which slots to insert the memory modules into. Often they are also colored differently and sometimes slightly offset from each other. Both help you to place the modules correctly according to the motherboard manufacturer’s specifications.
In addition, RAM slots differ between laptops and desktop computers. Notebooks mostly use SODIMM modules, which are shorter and smaller than the standard desktop DIMM variants. Most laptops also have only two RAM slots, which are tilted to one side to ensure that the modules are installed flat.
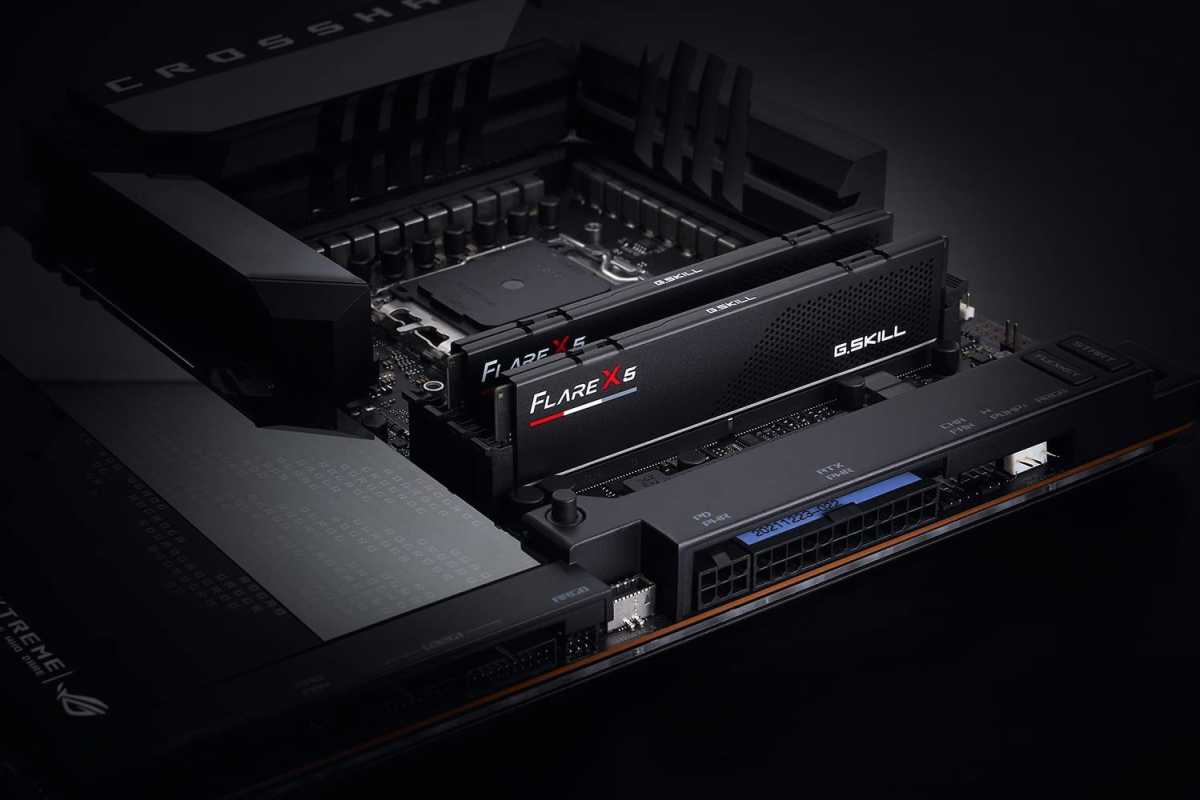

In dual-channel mode, the identically sized RAM modules must be in the correct RAM slots to avoid performance degradation.
Gskill
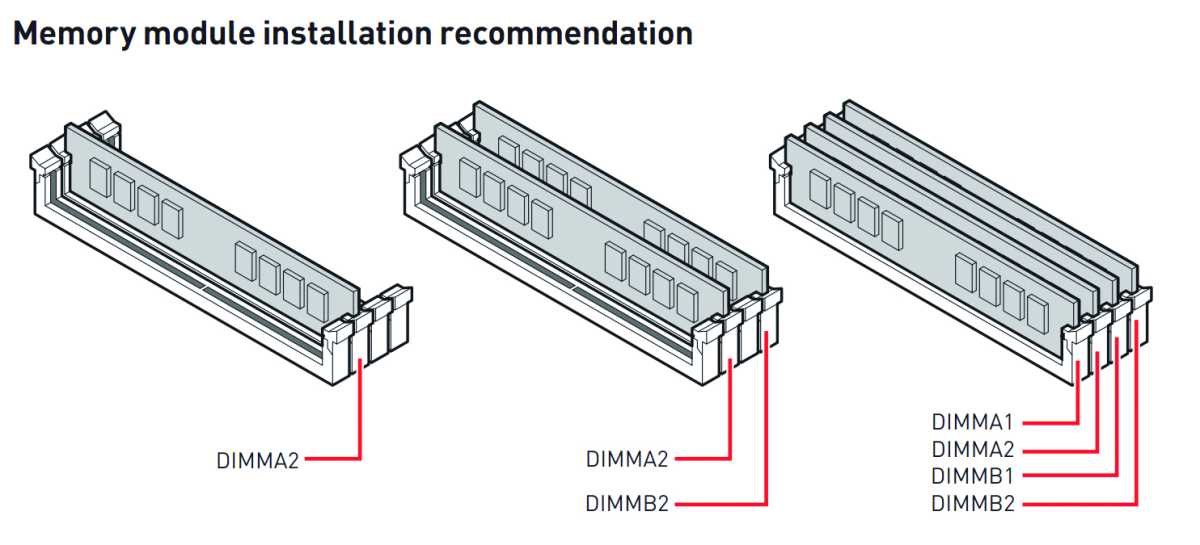
Choosing the right order of RAM slots can actually have a significant impact on memory performance, provided your motherboard supports dual-channel memory (most do). To take full advantage of multi-channel memory, a pair of RAM modules should be inserted into different memory channels. However, this is where the modules are often inserted incorrectly.
They must be inserted in the first and third slots, or the second and fourth slots, and not next to each other. It is always advisable to study the motherboard manual to find the recommended order of RAM slots. Following are some common dual-channel configurations: If your motherboard has two slots but you only have one module, you can put it in either slot.
If you have three slots and two modules, you should put the modules in the first and third slots. If you have four slots and one module, you can put the RAM in the first or fourth bank. If you have two memory bars in four slots, you should use the second and fourth slots. If you have four slots and four memory, you should insert a matching pair in the first and third slots and another matching pair in the second and fourth slots.
Refer to the mainboard manufacturer’s manual for the correct RAM slot assignment
Information. As a rule, you will find all possible plug-in variants here.
IDG
Dual-channel RAM should theoretically perform twice as well as single-channel RAM. In practice, however, this is rarely the case due to unavoidable bottlenecks in the system. It also depends on how well a game or the software is programmed to use the extra memory bandwidth.
Most benchmarks indicate an improvement of 20 to 30 percent when using a dual-channel memory configuration instead of a single-channel configuration — but only in terms of metrics such as frame rate in games. The correct installation of RAM in the appropriate slots is therefore a crucial factor for the optimal performance of your computer. It may seem trivial, but it can ultimately make a significant difference to the efficiency of your system.
Further RAM reading:
- How to choose the right RAM for your PC
- How to set up new computer RAM
- How to upgrade your laptop’s RAM
- How to enable XMP to run your RAM at full speed
- Should you upgrade your RAM? 5 things to consider
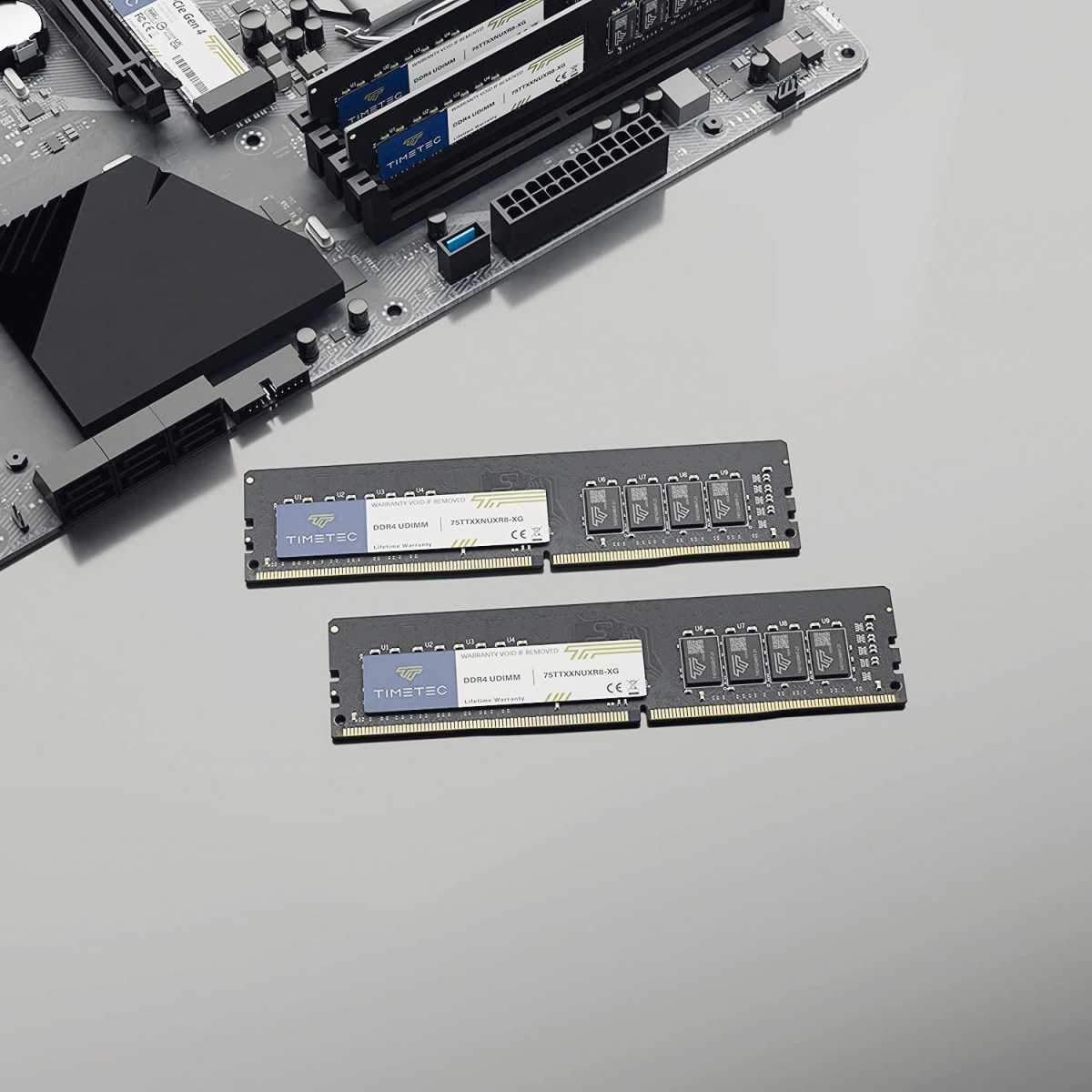

If you have four RAM slots, but only two dual-channel memory bars,
choose the second and fourth slots for maximum performance.Timetec
This article was translated from German to English and originally appeared on pcwelt.de.
